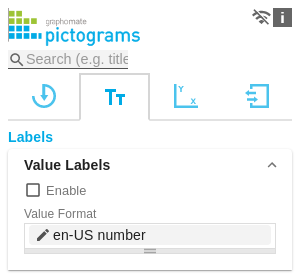
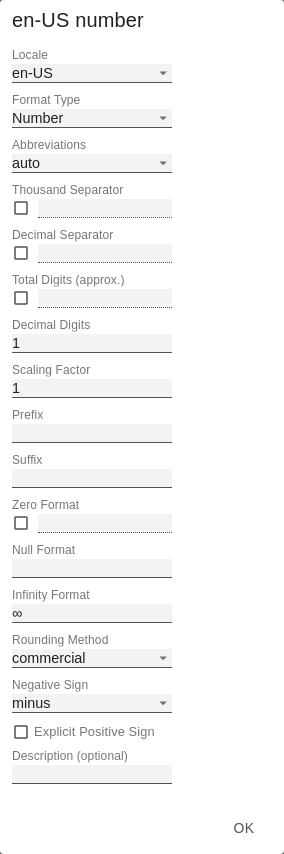
Value LabelsHere you can select whether you want value labels displayed. With the Value Format you define the way the values are displayed in the diagram area. You access the configuration by clicking on the element in the list. Define the number format using the following options: - Locale: Defines abbreviations, decimal and thousand separators for the respective language. You can choose between en, de, fr and auto.
- Format Type: Defines the type of number output. You can choose between number (decimal number), percent (percentage), ordinal (ordinal number) and Time (time unit).
- Abbreviations: Defines the type of abbreviations for all numbers to be formatted. You can choose between mean (abbreviation of the mean value), min (abbreviation of the minimum value), max (abbreviation of the maximum value), auto (best-suited abbreviation for the respective number), trillion (trillion abbreviation), billion (billion abbreviation), million, thousand and none (no abbreviation at all).
- Negative Sign: Defines how negative numbers are displayed. You can choose between minus, parenthesis, and none (no sign).
- Prefix: The input value is placed before the number.
- Suffix: The input value is placed after the number.
- Thousands Separator: Replaces the thousand separator set by the selected locale.
- Decimal Separator: Replaces the decimal separator set by the selected locale.
- Total Digits: Defines how many digits the number may consist of. Total Digits is prioritized over Decimal Digits.
- Decimal Digits: Defines how many decimal places of the formatted number are displayed.
- Scaling Factor: The value of each data point is multiplied by the entered number to scale values.
- Zero Format: When the checkbox is activated, any data value equal to 0 (the number zero) is replaced by the entered value.
- Null Format: Any data value that equals NULL (no value) is replaced by the entered value.
- Error Format: If a data value is undefined or the result of an arithmetic error such as dividing by 0 (zero), the data value is replaced by the entered value.
- Rounding Method: Defines the rounding method. You can choose between half up (23.5 → 24, -23.5 → -23), commercial (23.5 → 24, -23.5 → -24) and trim (23.5 → 23, -23.5 → 23).
- Explicit Positive Sign: Defines whether a positive number should always be preceded by a + (plus sign).
- Time Units: If Time has been specified for the format type, the time units can be set here. The default setting interprets data values as seconds and displays them as hours and minutes with decimal places in the format h:mm.m
- Description: Defines a description for the set configuration.
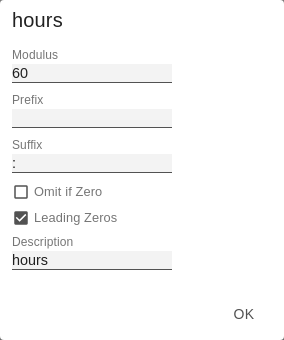
For the Format Type Time, a system of units can be configured with the help of the Time Units Property, which in the default setting consists of hours and minutes. Each number formatted in this way is then splitted in its values for each unit. The order of the unit list defines their relationship from the largest unit (top) to the smallest unit (bottom). Each unit contains the following options: - Modulus: defines the arithmetic relationship between the units. In terms of modular arithmetic, the number reflects how many entities of the next smaller unit fit into an entity of the current unit. If the current unit is the smallest of the unit system, the modulus establishes the reference to the raw value to be formatted. Thus, in the case of a unit system of hours and minutes with raw values that are given in minutes, the hours unit carries the modulus 60 and the minutes unit carries the modulus 1.
- Prefix: Defines the local prefix with which the value of this unit should begin. It can be used as a separator to values of larger units.
- Suffix: Defines the local suffix that should follow the value of this unit. For example, it can contain a unit abbreviation or be used as a separator to values of smaller units.
- Omit If Zero: Sets whether values of this unit should be omitted if they equal 0.
- Leading Zeros: Sets whether values of this unit should be displayed with one or more leading zeros (depending on the reference to the next larger unit).
- Description: Sets a description for the unit to make it easier to recognize in the list.
| |
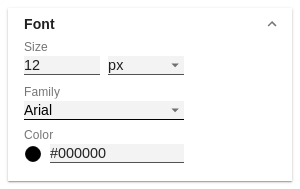
FontSizeSpecify the font size here. Select a CSS unit from the list (such as px, em). FamilyDefine the global font. You can choose between Arial, Tahoma, Lucida Console, Verdana and Calibri or type in the name of a font which is installed on your system. ColorSpecify the font color here. | |
TitleIf the Enable checkbox is activated, the title is displayed. Title TextEnter a Title for the pictograms here. Multiline texts will be rendered accordingly, i.e. the line break will be applied. The following HTML tags can be used for formatting: 'b', 'i', 'p', 'span', 'div', 'br', 'h1', 'h2', 'h3', 'h4', 'h5', 'h6', 'hr', 'ol', 'ul', 'li' and 'blockquote'. For the following result
ACME Ltd.
P&L by Segment
2021 this input is necessary: ACME Ltd.
<b>P&L</b> by <i>Segment</i>
2021 Font SizeSpecify the font size here. Select a CSS unit from the list (such as px, em). SpacingDefines the distance of the header area to the pictogram. Select a CSS unit from the list (such as px, em). | |
Category LabelsSuppress Repeating Category LabelsControls whether repetitive category labels should be hidden or displayed. Members in CategoriesSpecify whether the names of the members should be displayed in the category labels. Measures in CategoriesSpecify whether the member name of the measure/value dimension should be displayed. Hierarchical Category SpacingDetermines the distance between the hierarchical display of category labels. Select a CSS unit from the list (such as px, em). | |
Here you can define a text that appears below the pictogram. Font SizeSpecify the font size here. Select a CSS unit from the list (such as px, em). SpacingDefines the distance between the footer area and the pictogram. Select a CSS unit from the list (such as px, em). | |